A Central Hot Water System is a heating infrastructure that provides hot water to multiple locations within a building or facility from a centralized source. It is commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to efficiently supply hot water for various purposes, such as domestic use, space heating, and industrial processes. Central hot water systems offer several advantages, including energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, and consistent hot water supply.
Key components and features of a Central Hot Water System include:
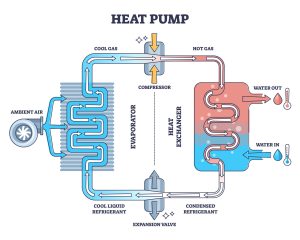
Heat Source: The heat source is the central element of the system that heats the water. Common heat sources include boilers, water heaters, heat pumps, solar thermal systems, or district heating networks.
Distribution Network: A network of pipes and circulation pumps distributes hot water from the heat source to different areas or points of use within the building. Insulated pipes help minimize heat loss during distribution.
Storage Tanks: In some central hot water systems, hot water is stored in large tanks to ensure a ready supply of hot water for immediate use. Storage tanks can be vertical or horizontal and may vary in size based on demand.
Circulation System: Circulation pumps ensure that hot water flows through the distribution network and reaches all points of use efficiently. Recirculation systems may be used to reduce waiting time for hot water at faucets.
Temperature Control: Thermostatic controls and valves regulate the temperature of the hot water to ensure it meets specific requirements for different applications.
Safety Measures: Safety features, such as pressure relief valves and temperature-limiting devices, are incorporated to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation.
Energy Efficiency: Central hot water systems can be designed for energy efficiency by using high-efficiency heat sources, insulation, temperature control strategies, and heat recovery systems.
Backup Systems: In case of heat source failure, backup heating systems may be integrated to ensure a continuous supply of hot water.
Maintenance and Service: Regular maintenance of the heat source, pumps, valves, and other components is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Scaling and Water Treatment: Proper water treatment is important to prevent scaling and mineral buildup in the system, which can reduce efficiency and cause damage.
Domestic and Commercial Applications: Central hot water systems are suitable for a range of applications, from providing hot water to individual apartments or homes to serving large commercial buildings, hotels, hospitals, and industrial facilities.
Integration with Other Systems: Central hot water systems can be integrated with other building systems, such as HVAC and energy management systems, for improved overall building performance.
Central hot water systems offer advantages in terms of energy savings, reduced equipment redundancy, and simplified maintenance compared to individual water heaters in each unit or area. However, the design and sizing of the system should consider factors such as peak demand, distribution layout, and energy source availability to ensure efficient and reliable hot water supply.



